Acne – subcutaneous nodules
back to main page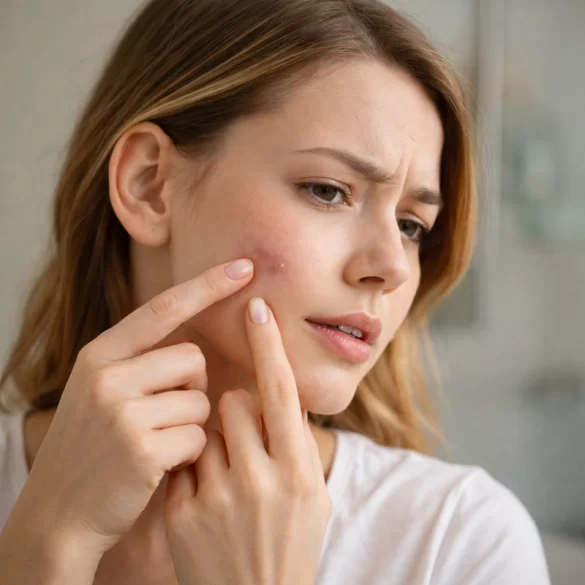
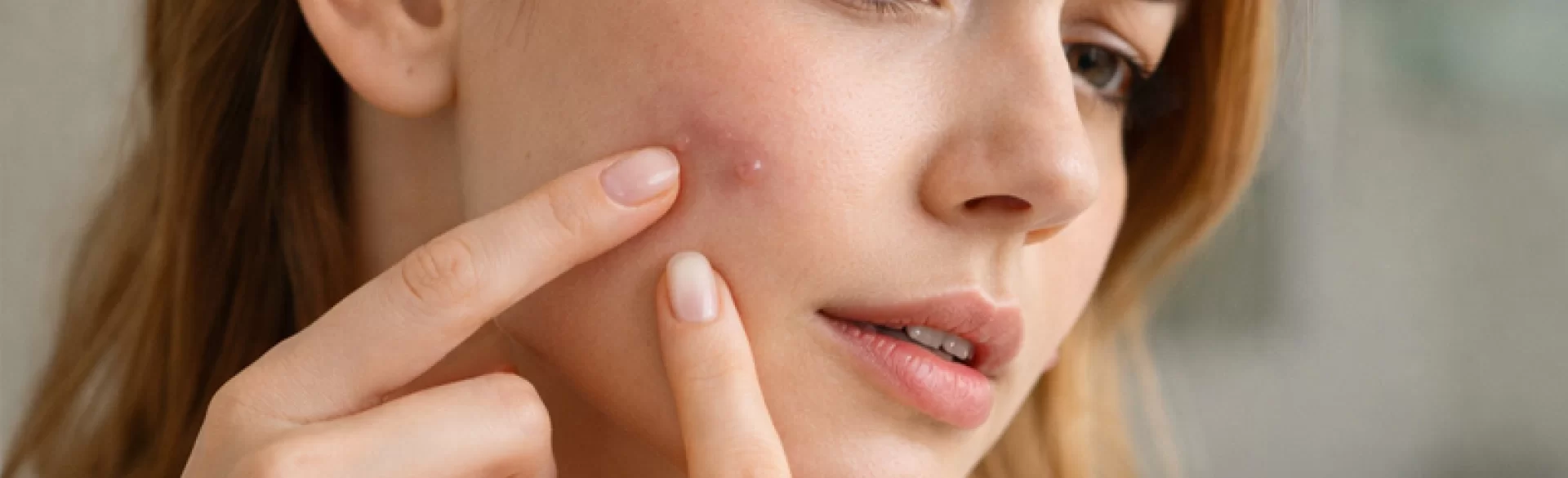
Subcutaneous nodules, commonly referred to as "under-skin pimples," are inflammatory lesions located deep within the hair follicle-sebaceous units. Unlike classic pustules, they do not have a visible opening on the skin's surface, making them more difficult to treat and often more painful. They most commonly appear on the face (jawline, chin, cheeks), but can also occur on the back, chest, and shoulders. Their presence can be episodic or chronic and is often associated with hormonal imbalances, improper skincare, or dermatological conditions. Untreated subcutaneous nodules can lead to the formation of acne scars and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Subcutaneous nodules – causes
The formation of subcutaneous nodules is a multifactorial process in which the disruption of sebaceous glands and the inflammatory response of the skin play a key role.
The most common causes include:
- Excessive sebum production – promotes the clogging of hair follicle openings.
- Hyperkeratinization – excessive skin keratinization leading to pore closure.
- Colonization by Cutibacterium acnes bacteria – these bacteria enhance the inflammatory response in the deeper layers of the skin.
- Hormonal imbalances – particularly fluctuations in androgens, typical during adolescence, polycystic ovary syndrome, or the menstrual cycle.
- Chronic stress – through increased cortisol secretion affects the activity of sebaceous glands.
- Improper skincare – using comedogenic cosmetics, aggressive mechanical peels, excessive skin cleansing.
- Dietary factors – a high glycemic index diet and an excess of dairy products can exacerbate changes in predisposed individuals.
- Genetic predispositions – the tendency to acne and inflammatory changes often has a familial nature.
It is worth noting that a single factor rarely acts in isolation – it is usually the result of the overlap of several mechanisms simultaneously.
Subcutaneous lumps – how to remove
Treatment of subcutaneous nodules requires a causal approach and patience, as these changes develop deep within the skin. Self-extraction is contraindicated – it increases the risk of infection, scarring, and the persistence of inflammation.
Therapeutic management includes:
1. Dermatological treatment
- preparations that normalize the keratinization of the epidermis,
- substances with anti-inflammatory and sebum-regulating effects,
- systemic therapy in selected cases when lesions are severe or recurrent.
2. Targeted skincare
- gentle but regular cleansing of the skin,
- use of non-comedogenic products,
- rebuilding the hydrolipid barrier to limit secondary irritation.
3. Dermatological and aesthetic procedures
- exfoliating procedures that control hyperkeratinization,
- light or energy therapies to reduce sebaceous gland activity,
- procedures that stimulate skin regeneration and reduce inflammation.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the correct diagnosis – subcutaneous nodules can be a symptom of both common acne and hormonal acne or inflammatory forms requiring different management.
Subcutaneous Nodules – Prevention
Prevention plays a key role in reducing the recurrence of subcutaneous lesions, especially in individuals prone to acne.
Preventive Recommendations:
- Regular, but gentle skincare tailored to the skin type.
- Avoidance of pore-clogging cosmetics, especially heavy foundations and creams with high mineral oil content.
- Protection of the skin barrier – excessive drying paradoxically increases sebum production.
- Hygiene of accessories that come into contact with the skin (brushes, sponges, phone).
- Control of stress and sleep, which have a real impact on hormonal balance.
- Balanced diet with limited highly processed products.
- Early response to initial changes – rapid implementation of treatment reduces the risk of deep inflammatory conditions developing.
Prevention does not entirely eliminate the risk but significantly reduces the frequency and severity of recurrences.
Treatments for subcutaneous nodules
Modern dermatology and aesthetic medicine offer procedures that effectively support the treatment of subcutaneous nodules, especially when standard care proves insufficient.
The most commonly used include:
- Exfoliating treatments with controlled penetration, which regulate the keratinization process and unblock hair follicle openings.
- Laser and light therapies, which reduce the activity of sebaceous glands and the number of bacteria responsible for inflammation.
- Medical-grade skin cleansing procedures, conducted without the risk of damage.
- Regenerative therapies, which improve healing and reduce the risk of acne scars.
- Procedures that normalize the function of oily and combination skin, used in therapeutic series.
Choosing treatments should always be preceded by a dermatological assessment, as not every subcutaneous nodule has the same underlying cause. Rational, staged treatment yields the best results and helps to avoid chronic aesthetic complications.

