Seborrhea
back to main page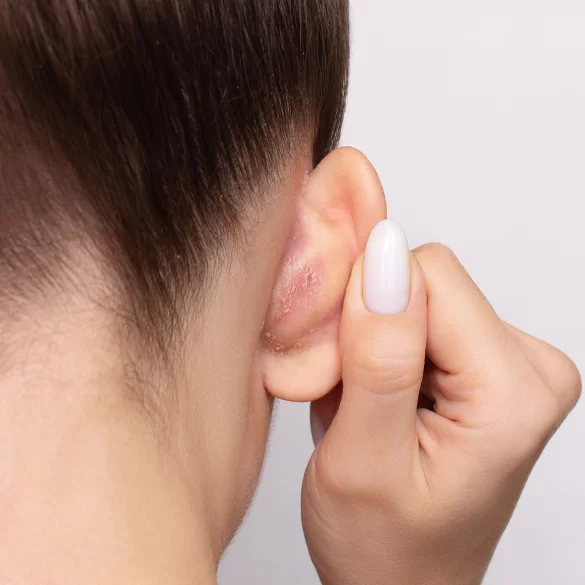
Seborrhea is a disorder of the sebaceous glands characterized by excessive sebum production – a lipid secretion that physiologically protects the skin and hair. This issue most commonly affects areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face (T-zone), chest, and upper back. Seborrhea is not a disease in itself but a functional state of the skin that can predispose to the development of secondary conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis, acne, or folliculitis. The severity of symptoms can vary and depends on numerous endogenous and environmental factors. This condition can occur at any age, but it is most frequently observed during periods of increased hormonal activity.
Seborrhea – what is it
Seborrhea is defined as a quantitative disorder of sebum secretion by the sebaceous glands, without the necessary coexistence of inflammation. Sebum mainly consists of triglycerides, wax esters, squalene, and free fatty acids, and plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin's hydrolipid barrier.
There are two primary types of seborrhea:
- Oily seborrhea – associated with the overproduction of sebum, leading to shiny skin, enlarged hair follicle openings, and greasy hair.
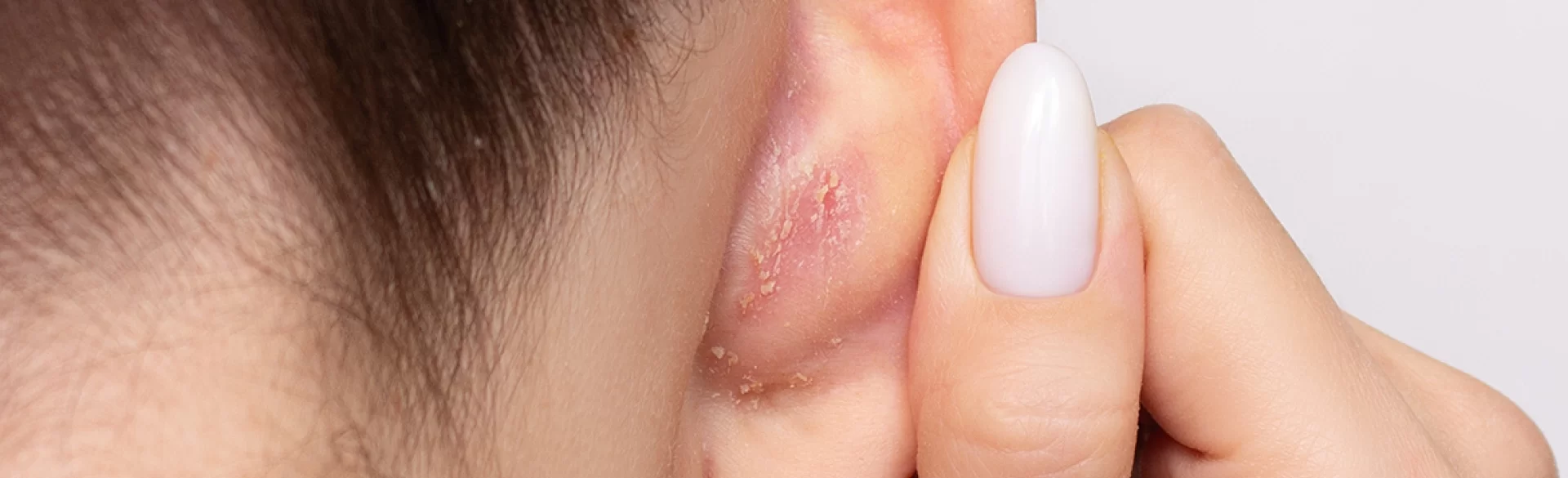
- Dry seborrhea – characterized by an altered composition of sebum and disrupted keratinization, often coexisting with excessive flaking of the epidermis.
Seborrhea has a chronic or recurrent nature, and its clinical presentation may vary depending on age, sex, hormonal status, and skin care.
Seborrhea – Causes
The etiology of seborrhea is multifactorial and involves interactions between the hormonal system, nervous system, and environmental factors. Androgens play a key role by stimulating the activity of sebaceous glands.
The most important causes and predisposing factors include:
- hormonal disorders (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, endocrine diseases),
- hypersensitivity of androgen receptors in the sebaceous glands,
- genetic factors – familial predispositions to increased gland activity,
- chronic stress and activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis,
- poor diet, especially rich in high glycemic index products and trans fats,
- inappropriate skin care, including aggressive detergents and excessive degreasing,
- environmental factors – humidity, temperature, air pollution.
Seborrhea can also coexist with neurological diseases and immunological disorders, confirming its complex pathophysiological basis.
Seborrhea – Symptoms
The clinical picture of seborrhea depends on the location and the degree of excessive sebum production. The symptoms are functional and aesthetic in nature, but in some cases, they may lead to dermatological complications.
The most commonly observed symptoms are:
- excessive skin shine, especially on the face,
- rapid greasing of the hair and scalp,
- enlarged hair follicle openings,
- tendency to develop blackheads,
- feeling of skin stickiness,
- in dry seborrhea: skin peeling and fine flaky dandruff.
In some patients, seborrhea serves as a basis for the development of:
- seborrheic dermatitis,
- acne vulgaris or adult acne,
- inflammatory conditions of hair follicles.
Seborrhea - Treatment
Therapeutic management of seborrhea is multi-stage and long-term. The goal of treatment is to normalize sebum secretion, improve skin barrier function, and reduce factors that exacerbate symptoms.
Treatment includes:
- appropriate dermatological care – sebo-regulating, non-comedogenic products with physiological pH,
- lifestyle modification (stress reduction, balanced diet),
- dermatological treatment in the presence of coexisting inflammatory skin diseases,
- in justified cases, systemic therapy aimed at hormonal or metabolic disorders.
It is important to avoid excessive degreasing of the skin, which paradoxically can lead to secondary stimulation of the sebaceous glands.
Seborrheic treatments
The classic dermatological procedures are complemented by aesthetic medicine and medical cosmetology procedures, aimed at regulating sebaceous gland activity and improving skin quality.
The most commonly used methods include:
- exfoliating treatments based on controlled exfoliation of the epidermis,
- therapies normalizing microcirculation and skin metabolism,
- treatments using light energy or electromagnetic waves to reduce sebaceous gland activity,
- cleansing and detoxifying procedures for the skin.
The selection of the method should be preceded by a detailed assessment of the skin condition, medical history, and analysis of factors exacerbating seborrhea. Procedural therapy is supportive and does not replace comprehensive causal treatment.

